Test Overview
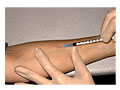
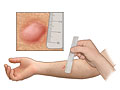
A tuberculin skin test (also called a Mantoux tuberculin test) is done to see if you have ever been exposed to tuberculosis (TB). The test is done by putting a small amount of TB protein (antigens) under the top layer of skin on your inner forearm. If you have ever been exposed to the TB bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), your skin will react to the antigens by developing a firm red bump at the site within 2 days.
The TB antigens used in a tuberculin skin test are called purified protein derivative (PPD). A measured amount of PPD in a shot is put under the top layer of skin on your forearm. This is a good test for finding a TB infection. It is often used when symptoms, screening, or testing, such as a chest X-ray, show that a person may have TB.
A tuberculin skin test cannot tell how long you have been infected with TB. It also cannot tell if the infection is latent (inactive) or if you have active TB that can be passed to others.
Current as of: April 30, 2024
© 2017-2025 Healthwise, Incorporated. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor.