Test Overview
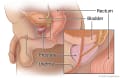
A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. PSA is released into the blood by the prostate, which is part of the male reproductive system. Healthy people have low amounts of PSA in the blood. The amount of PSA in the blood normally increases as the prostate enlarges with age. PSA may increase because of inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) or prostate cancer. An injury, a digital rectal exam, or sexual activity (ejaculation) may also briefly raise PSA levels.
Current as of: October 25, 2024
© 2017-2025 Healthwise, Incorporated. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor.