Test Overview
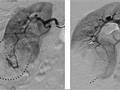
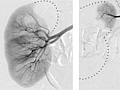
An angiogram is an X-ray test that uses dye and a camera to take pictures of the blood flow in an artery or a vein. An angiogram can be used to look at the arteries or veins in the head, arms, legs, chest, back, or belly. This test is done to look for problems in the arteries or veins.
An angiogram is done for many reasons. For example, you may have this test to find the source of bleeding, such as an ulcer. Or it may be done to look for blocked blood vessels in your lungs.
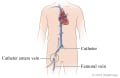
During an angiogram, the doctor will put a thin, flexible tube into a blood vessel in your groin or arm. This tube is called a catheter. The doctor guides the tube to the blood vessel that will be studied. Then a dye is injected through the tube to make the area easier to see. X-rays or pictures are taken of the area.
You will be given medicine to make you sleepy and comfortable during the test. You may or may not need to stay in the hospital overnight. You will stay in a room for at least a few hours to make sure the catheter site starts to heal.