Surgery Overview
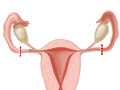
Tubal ligation is surgery to close your fallopian tubes. It's also called having your tubes tied.
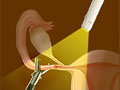
To close your tubes, the doctor may band, burn (cauterize), tie and cut, or clip them. The doctor may also completely remove the fallopian tubes. After this, an egg can't move down your tubes and can't be fertilized. This means you can't get pregnant.
This surgery can be done in two ways. In laparoscopic surgery, a doctor puts a lighted tube (scope) and other tools through a few small cuts. These cuts are called incisions. One is just below your belly button. The other is lower on your abdomen. After this surgery, you will probably stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 hours. You can likely go back to work in 2 to 7 days.
The other type of surgery is called open surgery(mini-laparotomy). In this surgery, the doctor makes a larger incision above your pubic hairline or below your belly button. You will probably stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days if you have this surgery. You can probably go back to work in about 1 to 2 weeks.
Surgery can be done right after you give birth (postpartum tubal ligation). Open surgery is usually used.
After the surgery, you should not be able to get pregnant. While there is a very small chance you could get pregnant, tubal ligation is a very reliable form of birth control.
Tubal ligation won't affect your menstrual cycle or when you start menopause. It also won't affect your desire for sex. But you could feel more relaxed about having sex. This is because you don't have to worry about getting pregnant.