Condition Basics
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a problem that happens when germs (called bacteria) get into the urinary tract and cause an infection.
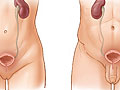
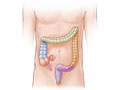
Your urinary tract is the system that makes urine and carries it out of your body. It includes your bladder and kidneys and the tubes that connect them.
Most UTIs are bladder infections. A bladder infection most often isn't serious if it's treated right away. But if you don't take care of a bladder infection, it can spread to your kidneys. A kidney infection is serious and can cause lasting damage.
What causes it?
UTIs are caused by germs (bacteria). The germs that most often cause these infections live in your large intestine and are found in your stool. The germs usually get into your urinary tract through your urethra. The urethra carries urine from your bladder to the outside of your body.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of a UTI may include pain or burning when you urinate. You may have an urge to urinate often, but you will usually pass only small amounts of urine. Your urine may be cloudy, look pink or red, or smell bad. You may feel pain in your lower belly or have flank pain.
How is it diagnosed?
To diagnose a UTI, your doctor will test a sample of your urine to see if it has germs that cause infections. Your doctor will also ask you about your past health and do a physical exam. If you have infections often, you may need more tests to find out why.
How is a UTI treated?
Antibiotics can cure most UTIs. It may help to drink lots of water and other fluids. Urinate often, and empty your bladder each time. For pain and burning, your doctor may advise you to take a medicine called phenazopyridine. If the UTI affects your kidneys or causes widespread infection, you may need hospital care.
How can you prevent a UTI?
There are some things you can do that may help prevent UTIs. For example, drinking more water may help. Take time to empty your bladder as much as you can when you urinate. If you have a female urinary tract and you are sexually active, make sure to urinate soon after you have sex.