Condition Basics
What is colorectal cancer?
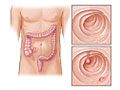
Colorectal cancer happens when abnormal cells grow in your colon or rectum. These cells often form in growths called polyps. Not all polyps become cancer. Colorectal cancer is also called colon or rectal cancer, depending on where it's located. Your risk for colorectal cancer gets higher as you get older.
What causes it?
The exact cause of colorectal cancer is not known. Most cases begin in polyps, which are small growths inside the colon or rectum. Colon polyps are very common. Some polyps can turn into cancer. But if they are found early, usually through routine screening tests, they can be removed before they do.
What are the symptoms?
Colorectal cancer usually doesn't cause symptoms until after it has started to spread. The most common symptoms include blood in your stools and very dark stools. You may have more frequent bowel movements. Or you may feel like your bowels aren't emptying completely. Other symptoms may include belly or rectal pain.
How is it diagnosed?
If your doctor thinks you may have colorectal cancer, you'll be asked about your medical history and have a physical exam. You may have blood tests. Your doctor may use a lighted scope to view the inside of your colon (colonoscopy) and take a biopsy. You may also have imaging tests like a CT scan.
How is colorectal cancer treated?
Treatment for colorectal cancer is based on the stage and location of the cancer. It's also based on other things, such as your overall health. Most people have surgery to remove the cancer. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both may also be used. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may be an option.